Vibecheck Phase 2
Aufgrund der technischen Terminologie ist der Projektplan in Englisch verfasst.
Status Quo
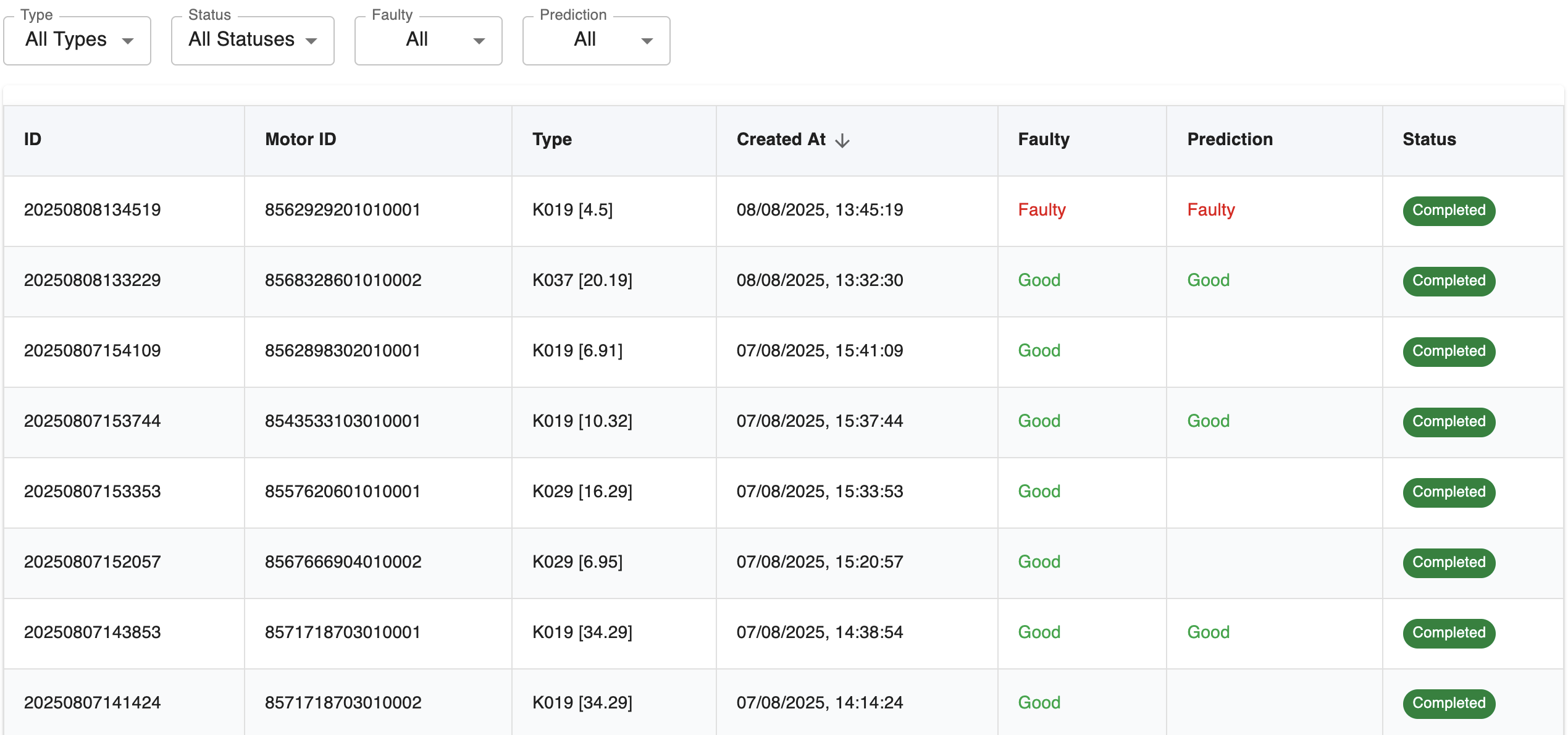
Motius successfully completed a Proof of Concept (as of August 2025) of the Vibecheck acoustic end-of-line testing.
- Structure-borne sound microphone: Capture of sound signals during ~20s dynamic test profile (two directions & two speeds, 4-5s each)
- ML algorithm: Optimized classification through extended datasets and augmentation
- Test sequence: Dynamic profile with forward/backward rotation at various RPM, integrated into LabVIEW & TestStand
- Simple User Interface: Workers can confirm / correct results, with a simple green/red display in LabVIEW
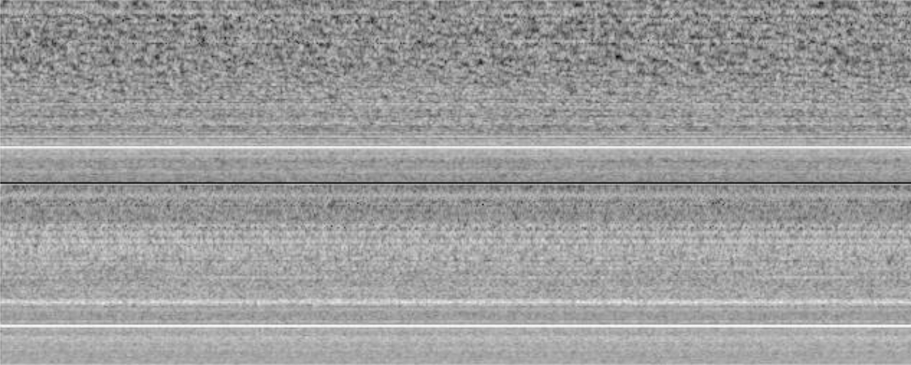
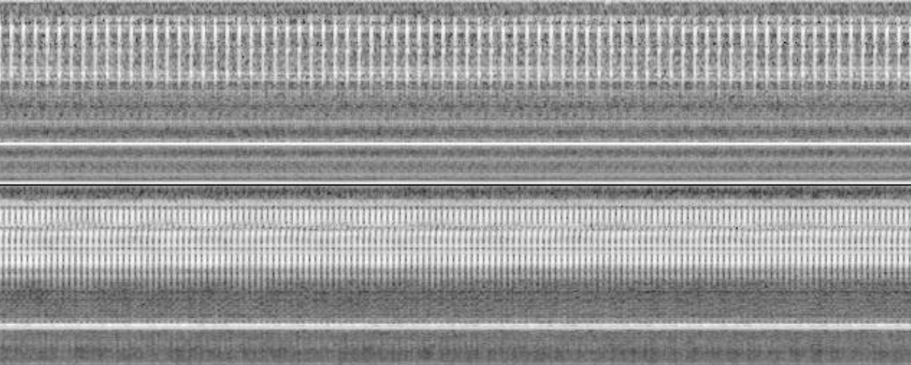
- Data processing: .wav (10s samples) → Log-Mel spectrograms (up to 8kHz) → CNN/Autoencoder
- K series gearbox: PoC was validated on K series helical-bevel gear motors
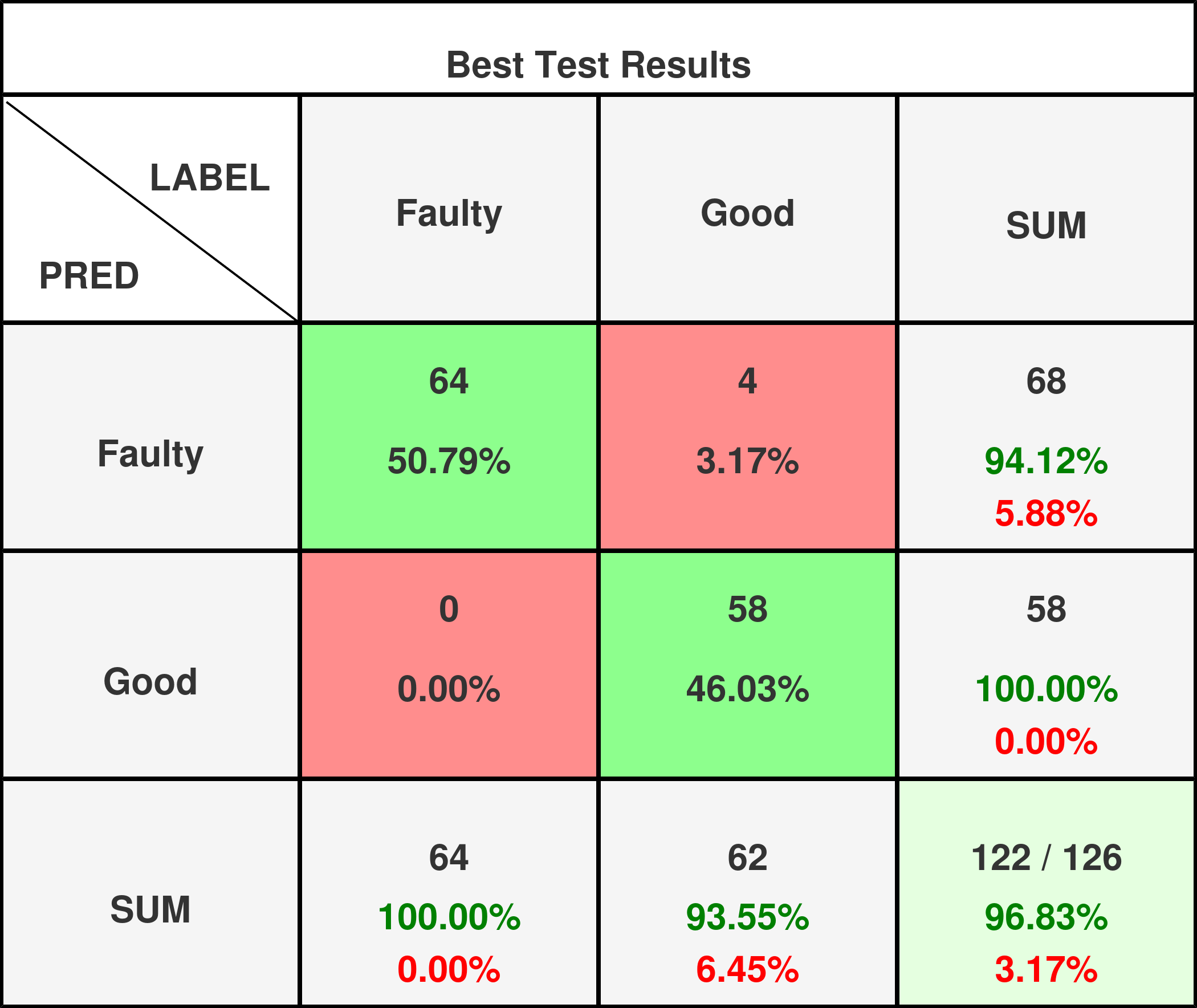
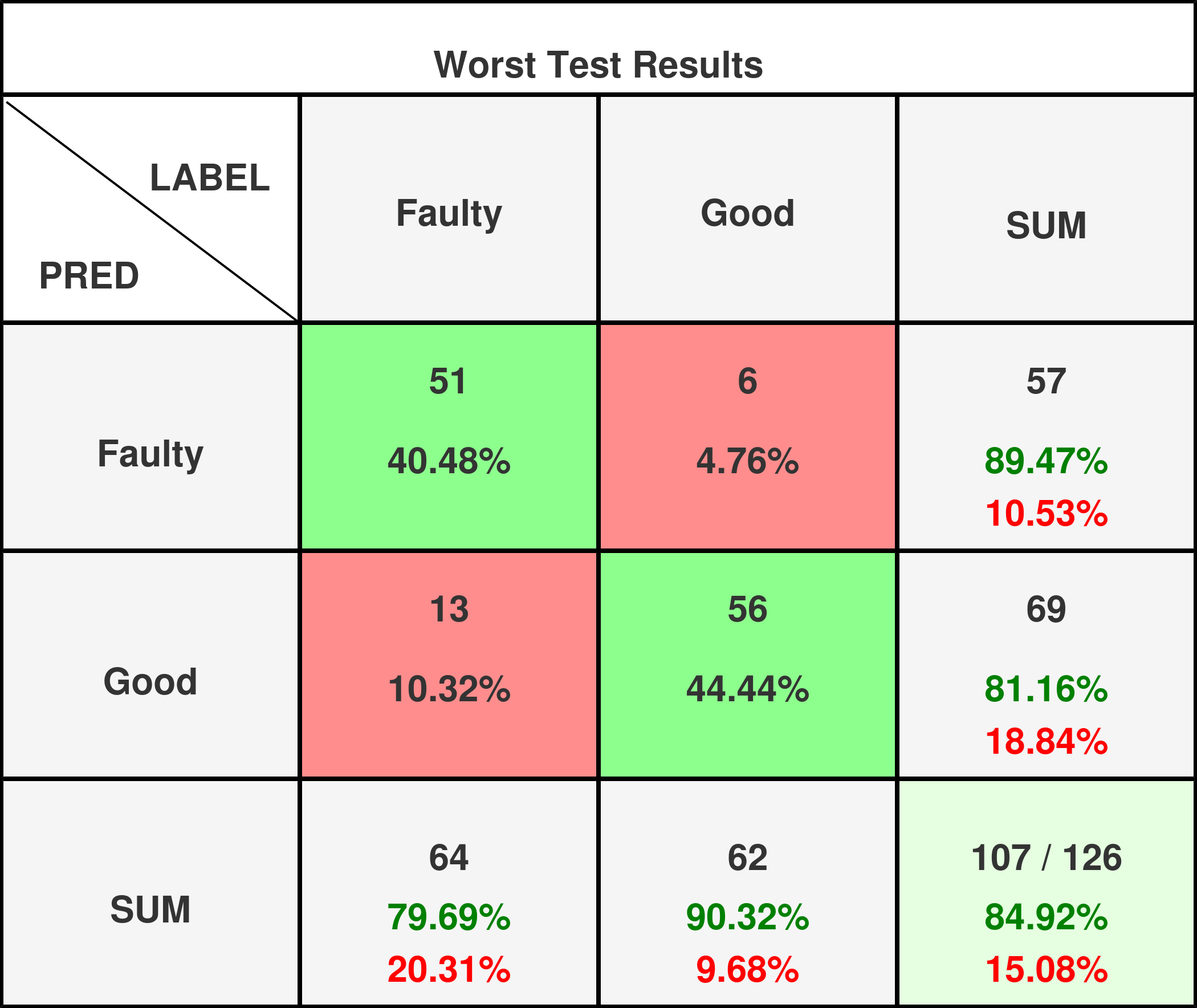
Based on 650+ experiments, as of August 2025, we achieved a reliable OK/Not OK classification with >90% accuracy (Confusion Matrix validated).
Defect Types
| Classification | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| OK | No audible damage | 90.29% |
| Ticks | Gear damage, scratches on tooth surfaces | 4.05% |
| General noise | Bearing damage, dirt in the gearbox | 5.66% |
- Input: .wav recordings from 20s dynamic motor test sequences
- Preprocessing: 5s sample extraction with overlap
- Feature Extraction: Log-Mel spectrograms (max frequency: 8kHz)
- Normalization: Per-sample spectrogram normalization
- Time-Frequency Representation: Horizontal time axis, vertical frequency axis
Dataset Characteristics
| Category | Count | Percentage | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valid Experiments | 577 | 76.63% | Clean, properly labeled data |
| Microphone Issues | 122 | 16.20% | RMS threshold filtering |
| Mislabeled Cases | 54 | 7.17% | Manual expert correction |
The comparatively low percentage of valid experiments points to a need for automation.
| Defect vs. Normal | Count | Percentage | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defect | 56 | 9.71% | Limits the data that can be used |
| Normal | 521 | 90.29% |
The model training required a balanced dataset, which means that roughly the same amount of defect samples should be used.
| Training Set | Count | Percentage | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defect Samples Used | 67 | 50.38% | All valid defect experiments |
| Normal Samples Used | 66 | 49.62% | Similar number of samples for balance |
Performance Metrics on Test Set
Performance metrics are only calculated for valid experiments:
- Sensitivity (Recall): ~89-94% - Critical for catching defects
- Specificity: ~81-100% - Important to minimize false alarms
- F1-Score: ~84-97% - Balanced performance indicator
Current IT Integration
- Connectivity & Deployment: Direct network connection to backend running in Motius AWS infrastructure
- Test bench integration: Custom Python module is called in the test process
- UI: Labelling interface, display of results with green/red status, allow marking experiments as irrelevant, and highlight important information (such as spectrograms that lead to not-OK classifications)
- Workflow:
- 20s total data recording time, ~30s in total (including processing times)
- Additional reminder pop-up for attaching the body sound sensor reduced the number of invalid experiments from 25% to 5%
- Laser vibrometer: Comparative studies show equivalent results to structure-borne sound microphone
- Analysis App: VibeCheck Web App for manually analyzing, re-labelling datapoints, and marking experiments as invalid (thereby excluding them from training)
Laser Vibrometer
We benchmarked a Polytec laser vibrometer with auto-focus against the structure-borne sound microphone. The vibrometer provided similar sensor readings, without contact to the motor.
Phase 2
Extending VibeCheck Algorithm
The successfully validated PoC algorithm currently supports one gearbox type (bevel gear motors). In Phase 2, we want to support a larger variety of products, and roll out to multiple quality cells:
- Extended datasets: Further training with additional experiments for bevel gear transmissions
- Data augmentation: Audio augmentation (Pitch, Time Stretch) + spectrogram augmentation (Zoom, Brightness, Mixup, Erasing)
- The augmentation can improve the model generalization capability and can also enforce that the model learns features instead of memorizing training data features
- Data augmentation will be especially helpful for training new model versions for new gearbox types, which initially only have a small dataset
- Continuous learning: Automatic model updates based on new production data
- Performance monitoring: Continuous monitoring of classification accuracy
- Explainable AI: Feature importance and decision visualization for experts
- Historic data: Show history of experiments and model performance
- Invalid experiment detection: Additional script or model for detecting faulty experiments
- RMS Threshold: Detect microphone disconnect (sound intensity too low)
- Spectral Analysis: Identify unusual frequency patterns
- Future Enhancement: Dedicated ML model for experiment validation
- Advanced Architectures: Research transformer models for sequence modeling
Data Augmentation Strategy
Audio-level Augmentation
- Pitch shifting (±0-20%)
- Time stretching (±0-30%)
- Noise injection (SNR: 20-40dB)
Spectrogram-level Augmentation
- Zoom augmentation (random cropping/erasing/scaling)
- Brightness/contrast variation
- MixUp: Linear interpolation between samples
Model Architecture
Before scaling to more cells, the team needs to decide whether to extend a single model or train multiple gearbox-specific models.
| Approach | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Extended Single Model | Less training effort Simpler maintenance Faster rollout |
Possibly lower precision More complex feature engineering |
| Motor-Specific Models | Higher precision per motor type Specialized features Better scalability |
More training effort More complex pipeline More data required |
The team will likely train multiple models and test their performance compared to a single, bigger model.
Additionally, the architecture of the models could be adapted, after the first tests:
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
- Input: Log-Mel spectrograms as 2D images
- Architecture: Multi-layer CNN with attention mechanisms
- Output: Binary classification (OK/Not OK)
Autoencoder Approach
- Unsupervised pre-training for anomaly detection
- Reconstruction error as anomaly score
- Especially useful for rare defect types
Model Training Infrastructure
Even if the team decides to only train one model, a production deployment requires more infrastructure than the current PoC.
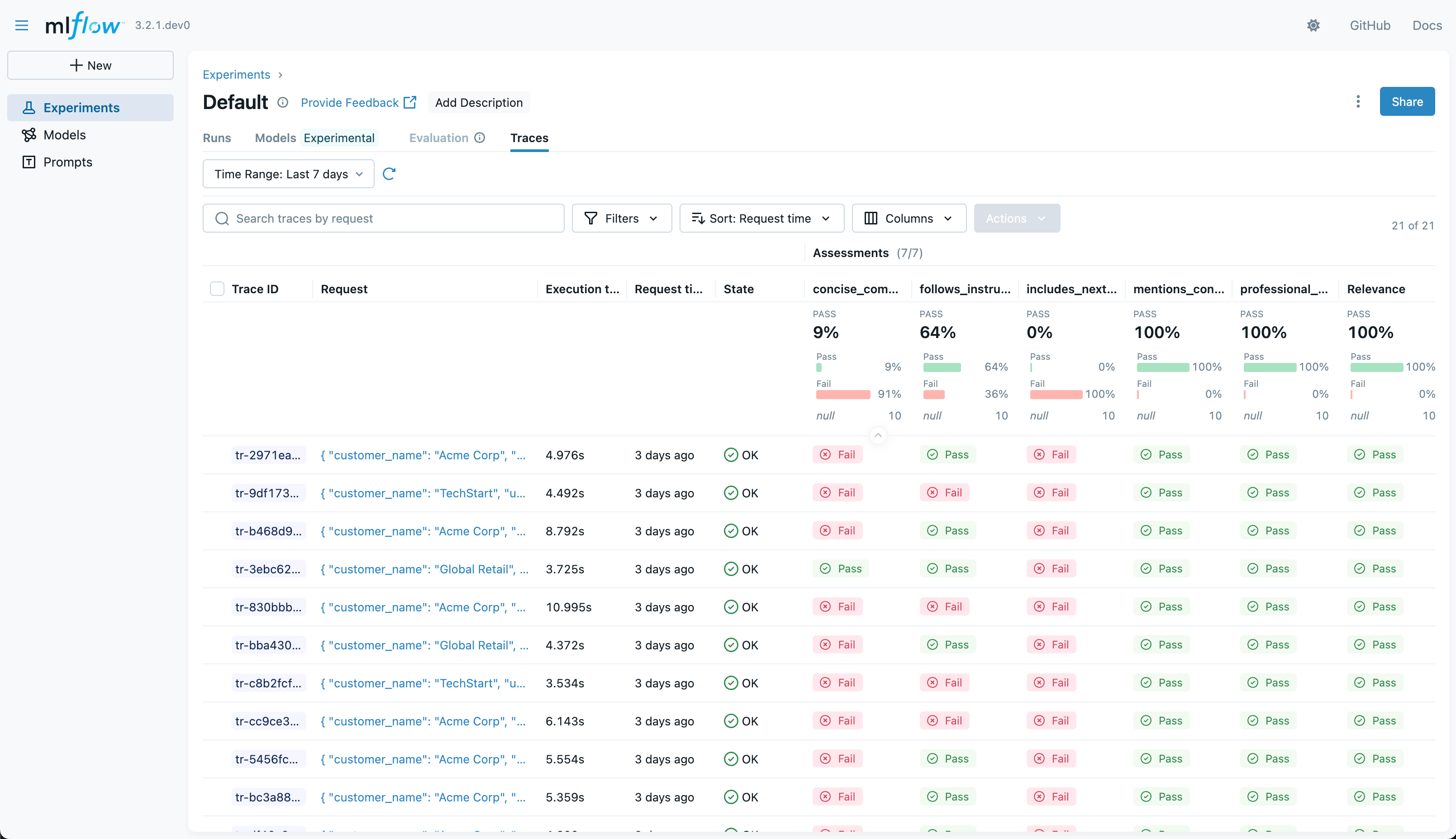
Example user interface for viewing experiments in MLflow
MLflow is an open-source platform for managing machine learning models. It can tie into existing PoC infrastructure (storage, database) and add model versioning, training with new data, and monitoring performance.
graph TB
classDef primary fill:#64CEE4,stroke:#64CEE4,stroke-width:2px,rx:10px
classDef default fill:none,stroke:#64CEE4,stroke-width:2px,rx:10px
classDef defaultBackground fill:#FFFFFF44,stroke:none,rx:20px
classDef primaryBackground fill:#23BAD933,stroke:none,rx:20px
subgraph Gearbox["Quality Cell"]
GB1[K-Series Gearboxmotor]
GB2[S-Series Gearboxmotor]
GB3[Servomotor]
AUDIO[Sensor]
TS[TestStand Python Node]
end
subgraph Web["Web Services"]
ADMIN[VibeCheck Admin Interface]
REST[VibeCheck REST API]
UI[MLflow Admin Interface]
end
subgraph MLflow["MLflow Tracking Server"]
MLT[MLflow Tracking Server]
MLB[MLflow Backend]
subgraph Model["Model Registry"]
MR[MLflow Model Registry]
V1[Model v1.0<br/>K-Series]
V2[Model v2.0<br/>K-Series]
V3[Model v1.0<br/>S-Series]
end
end
subgraph "Storage"
S3[MinIO<br />S3-compaible storage]
DB[Database]
ARTIFACTS[Model Artifacts<br/>- Trained Models<br/>- Feature Extractors<br/>- Preprocessors]
LOGS[Training Logs<br/>- Metrics<br/>- Parameters<br/>- Audio Samples]
end
Gearbox:::primaryBackground
Web:::primaryBackground
MLflow:::primaryBackground
Storage:::primaryBackground
Model:::defaultBackground
%% Connections
TS <-->|API Request<br/>Sensor Data| REST
REST <-->|API Request<br/>Model Inference| MLT
MLT -->|Fetch Model| MR
MR --->|Load Artifacts| S3
S3 -->|Model Files| MLT
MLB --->|SQL| DB
ADMIN --->|SQL| DB
%% Model versions
MR --> V1
MR --> V2
MR --> V3
%% Storage connections
MLT --->|Store Artifacts| S3
S3 --> ARTIFACTS
S3 --> LOGS
%% UI connections
UI -->|View Models<br/>Compare Versions| MR
UI -->|View Metrics| MLT
UI --> MLB
%% Gearbox data flow
GB1 --> AUDIO
GB2 --> AUDIO
GB3 --> AUDIO
AUDIO -->|Input Features| TS
class GB1,AUDIO,TS,ADMIN,REST,S3,DB,ARTIFACTS,V1 primaryHighlighted components in blue are already in place from the PoC, the other components will be added in Phase 2.
Deploying to SEW IT Infrastructure
Next, the algorithm needs to be deployed in SEW's IT infrastructure:
- VM vs Cloud: Decide with an expert from SEW's IT whether we deploy to Azure or into a VM
- Database & Storage Migration: Database and *.wav file storage needs to move to either Azure or a VM
- Model Versioning: Traceable versioning with rollback functionality
For the deployment, SEW needs to provide infrastructure with these parameters:
| Resource | Requirement | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Usage | 16GB RAM | Required for model loading and preprocessing pipeline in memory |
| CPU Requirements | 4 CPU cores | Models run without GPU, which means multiple cores help run multiple tests in parallel |
| Disk Usage | 1TB | Mostly for storing historical data and model versions |
| GPU | 16GB VRAM | Training a model with 650+ samples (PoC scope) takes ~30min on a GPU, >5h without it |
On Azure, the resources can be split into training & inference. Training only happens infrequently, in batches. Therefore, we can run training on separate resources that are billed by hour.
For training & inference on-premise we propose one bigger VM with enough resources to do both tasks.
Test Strategy
The deployed algorithm then needs to be tested on new product types and in new quality cells:
- Iterative Testing: Multiple test cycles with SEW experts
- Model validation: Confusion Matrix validation against SEW expert classifications
- False Negative Prevention: Testing & model validation need to ensure that false negatives are very unlikely
- False Positive Minimization: Too many false positives lead to additional manual work
- Performance Benchmarks: At least 90% classification accuracy
- Integration Testing: Complete LabVIEW pipeline validation
To structure this testing, the team will create an updated test strategy for a production-ready rollout.
Rollout to new Quality Cells and Product Types
An improved ML algorithm, hosted on SEW infrastructure, after proper testing enables SEW to roll out VibeCheck on their own:
- A process owner at SEW installs the required sensor and TestStand software in a new quality cell
- In the VibeCheck admin interface, they assign a model to the new quality cell, or create a new model version in MLflow (for example for a new gearbox type)
- During training, the TestStand user interface in the new quality cell shows the worker the normal manual acoustic testing routine, but starts recording data and creating a training data set
- Gearbox motors marked as defective go to a repair cell, where repair technicians diagnose & repair the problem
- Data from these diagnoses is imported into the VibeCheck dataset as well, to correct possible mislabeling by workers, and to increase the number of samples of defective motors
- When enough data is available (at least 50 defective samples), a model is trained automatically in MLflow and the TestStand user interface begins showing prediction results
- After some more validation with the worker, the model can work autonomously and only call in workers for defective or low-confidence results
Documentation and training materials will be created by the team for the first rollout, and improved during the first run by SEW.
Documentation includes:
| Documentation Type | Target Audience | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Admin Guide | Process owners | Step by step guide for creating new quality cell deployments, including creating new ML model variants in MLFlow |
| User Guide | Workers | Accessible from TestStand, probably in a web interface or as a PDF |
| Troubleshooting Guide | Workers and process owners | Common issues such as microphone disconnects and how to fix them |
Integration Requirements & Success Criteria
The MoSCoW method is a prioritization technique for requirements:
- Must have: Critical requirements that are non-negotiable for project success
- Should have: Important features that are highly desirable but not absolutely critical
- Could have: Nice-to-have features that would add value but can be deferred if necessary
- Won't have: Items explicitly excluded from the current scope but may be considered in future iterations
| Requirement | Priority | Description | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Existing HTTP Integration | Must | Use of already implemented MES-HTTP interface | Integration working |
| Python Integration | Must | Use of already implemented TestStand Python integration | Python calls successful |
| Data Flow | Must | Sensor → TestStand → HTTP → ML-Service → Result back | End-to-end data flow |
| Recording duration | Must | Less than 30s run time for the audio analysis | < 30s analysis time |
| NI Measurement Hardware | Must | Integration with existing NI DAQmx infrastructure | Hardware integration |
| Model accuracy | Must | Classification accuracy target | > 90% accuracy |
| False positive rate | Must | Minimize incorrect failure classifications | < 2% false negative rate |
| CI/CD Pipeline | Must | Continuous integration & deployment in SEW infrastructure | Automated deployments |
| Model Versioning | Must | Support for different gearbox types with version management | Multiple models managed |
| Logging & Error Tracing | Must | Comprehensive logging system for debugging and monitoring | All errors tracked |
| Multi-cell Support | Must | Infrastructure supporting continuous learning across multiple quality cells | 3+ cells operational |
| Functional Safety | Must | Safety concept for production deployment | Safety approval obtained |
| Laser Vibrometer | Must | Could replace body sound sensors with laser vibrometer, if easier to automate | Alternative sensor option |
| Performance | Should | Inference time target | < 1s inference time |
| System availability | Should | System uptime target | > 99% uptime |
| Body-Sound Microphone | Should | Contact-based sensors (already validated in EOL Cell 2) | Sensor validation |
| User Interface | Should | Green/Red display in LabVIEW with correction workflow for false positives | UI functionality |
| Order-XML Integration | Should | Automatic parameter extraction for dynamic profiles | Auto parameter extraction |
| Standardization | Should | Uniform setup based on EOL Cell 2 pilot experiences | Consistent setup |
| Data Augmentation | Should | Improved data augmentation for better model training | Enhanced model robustness |
| Performance Metrics | Should | Established metrics for model validation and monitoring | KPIs defined & tracked |
| Data Acquisition Monitor | Should | Detect issues with data acquisition and warning workers | Alert system operational |
| Documentation | Should | User handbook and deployment procedures for SEW process owners | Complete documentation |
| Integration Testing | Should | Complete testing in office environment before production | Tests passed |
| Minimal Rollout Effort | Could | TestStand setup + DAQ + body sound sensor or vibrometer installation per cell | TBD rollout time per cell |
| Worker Integration | Could | Inspector interface with pop-up labeling implemented on EOL PCs | Worker interface active |
| Production Monitoring | Could | One week monitoring period for all deployed cells | 7-day stability verified |
| Automation | Won't | Automating data acquisition is not part of this project | - |
Phase 2 Summary
-
Production-Ready ML Algorithm
Robust algorithm validated across multiple gearbox types with >90% accuracy
-
Automated Training Pipeline
Continuous learning system with automatic model updates and deployment
-
Performance Monitoring
Real-time accuracy tracking and anomaly detection across quality cells
-
Multi-Cell Operation
System successfully deployed and operational in two additional quality cells
-
Rollout Documentation
Complete handbooks and infrastructure for future in-house expansion to additional cells
-
Show positive ROI
Pre-filtering & reliable classification lead to a significant reduction in manual testing time and costs
Roadmap
---
config:
gantt:
barGap: 10
fontSize: 18
sectionFontSize: 18
barHeight: 40
leftPadding: 200
numberSectionStyles: 2
---
gantt
dateFormat X
axisFormat Sprint %s
tickInterval 1s
section Infrastructure
SEW#colon; Provide access to infrastructure :crit, infra0, 0, 1s
Simplify TestStand & LabVIEW integration :infra4, 0, 2s
Setup continuous learning infrastructure :infra1, 0, 3s
Setup model versioning & monitoring infrastructure :infra2, 1, 1s
IT Deployment at SEW :infra3, 2, 1s
section Machine Learning
Improve data augmentation :ml1, 0, 1s
Model versioning for gearbox types :ml3, 0, 3s
SEW#colon; Decide on further quality cell locations :crit, ml0, 1, 1s
Develop model validation & issue detection :ml2, after ml1, 2s
Rollout to 2nd & 3rd cell :vert, ml5, after ml2, 0
Performance monitoring system :ml4, after ml2, 1s
Testing with 2nd gearbox type in 2nd cell :ml6, after ml2, 2s
Develop CV algorithm for sensor placement :ml7, 2, 1s
section Deployment & Rollout
Document rollout procedures :deploy1, 0, 2s
Create user handbook & UI info :deploy2, after deploy1, 1s
Support rollout to additional cells :deploy3, after deploy1, 2sRed tasks in the GANTT roadmap are tasks that require input from SEW:
| Task | Sprint | SEW Action Required | Impact on Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provide access to IT infrastructure | 1 | Grant access to SEW IT systems, provide VM or container infrastructure | Blocks all deployment activities |
| Decide on further quality cell locations | 2 | Select 2 additional quality cells for VibeCheck rollout | Blocks testing and further development of model |
| Support deployment in Graben-Neudorf | 4 - 6 | Provide support for new quality cell setups | Required for physical deployment and testing |
Work packages
| Work Package | Duration |
|---|---|
| Setup infrastructure for multiple quality cells | 9 Days |
| Data update and analysis | 1 Days |
| Allow multiple runs per motor, link between runs | 1 Days |
| Highlight spectrograms that lead to not-OK classification | 1 Days |
| Setup performance metrics & model validation | 4 Days |
| Improve invalid experiment detection, mark as invalid and exclude from training | 3 Days |
| Implement workflow in TestStand to repeat experiment when an invalid experiment is detected | 2 Days |
| Data training format exploration | 1 Days |
| Improve data augmentation | 2 Days |
| Model training, comparison and iteration | 3 Days |
| Setup rules for model switching | 2 Days |
| Setup continuous-learning infrastructure | 4 Days |
| Allow selecting laser vibrometer or body sound sensor | 5 Days |
| Integrate laser vibrometer SDK, automate data acquisition & training | 11 Days |
| Implement data acquisition and validation for continuous learning | 4 Days |
| Implement model performance monitoring for continuous learning | 5 Days |
| Continuous integration & deployment in SEW infrastructure | 5 Days |
| Allow read-only external connections with SEW intranet to database with ODBC | 1 Days |
| Simplify TestStand & LabVIEW integration | 4 Days |
| Integrate data from repair station, parse non.structured text descriptions, validate Not OK labels from workers | 6 Days |
| Add admin interface to manage models and rules (which gearbox type goes to which model) | 6 Days |
| Implement & test model versioning for different gearbox types | 12 Days |
| Setup & test logging and error tracing | 2 Days |
| Detecting issues with data acquisition and warning workers | 5 Days |
| Support rollout to two additional quality cells | 8 Days |
| Document rollout & deployment procedures for SEW process owners | 3 Days |
| Create a user handbook & add information in the UI | 3 Days |
| Testing & validation with new gearbox type in new quality cells | 3 Days |
| Testing & monitoring of third cell over one week | 8 Days |
| Meetings & Project Management | 14 Days |
| Total Duration | 138 Days |
Rollen und Kosten
Rollen, Kosten, und der rechtliche Rahmen sind wieder in Deutsch verfasst.
| Rolle | Level | Tagessatz | Tage | Gesamtkosten |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Engineer | Technology Specialist III | 1,008.00 € | 54.00 Tage | 54,432.00 € |
| Software Engineer | Technology Specialist IV | 1,120.00 € | 66.00 Tage | 73,920.00 € |
| Mechanical Engineer | Technology Specialist III | 1,008.00 € | 4.00 Tage | 4,032.00 € |
| Project Owner | Project Management IV | 1,344.00 € | 14.00 Tage | 18,816.00 € |
| Gesamtkosten Entwicklung | 151,200.00 € | |||
| Reisekosten | 7,773.91 € | |||
| Fixkosten | 10,000.00 € | |||
| Gesamtkosten Netto | 168,973.91 € | |||
| Steuer (19%) | 32,105.04 € | |||
| Gesamtkosten Brutto | 201,078.96 € | |||
Hardware Kosten sind nicht Teil des Angebots.
Rate Card
Es gilt die Rate Card aus dem Rahmenvertrag, Stand 2025:
| Bereich | Titel | Level | Stundensatz | Tagessatz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Specialist | Senior Lead Tech Specialist | Technology Specialist VI | 180.00 € | 1,440.00 € |
| Lead Tech Specialist | Technology Specialist V | 161.00 € | 1,288.00 € | |
| Senior Tech Specialist | Technology Specialist IV | 140.00 € | 1,120.00 € | |
| Tech Specialist | Technology Specialist III | 126.00 € | 1,008.00 € | |
| Associate Tech Specialist | Technology Specialist III | 112.00 € | 896.00 € | |
| Developer | Technology Specialist I | 84.00 € | 672.00 € | |
| Project Management | Partner | Project Management VI | 230.00 € | 1,840.00 € |
| Senior Technical Executive | Project Management V | 187.00 € | 1,496.00 € | |
| Technical Executive | Project Management IV | 168.00 € | 1,344.00 € | |
| Senior Project Owner | Project Management III | 149.00 € | 1,192.00 € | |
| Project Owner | Project Management II | 133.00 € | 1,064.00 € | |
| Associate Project Owner | Project Management I | 112.00 € | 896.00 € |
Die oben skizzierten Projektrollen stellen ein Referenzteam dar. Sollte es bei der Besetzung der Projektrollen zu Abweichungen kommen, gilt folgende Rate Card. Das Projektvolumen bleibt unberührt.